Customer Services - Power Quality (PQ) Contracts Function
Contents
The purpose of the power quality contracts
enterprise activity is to enable a mechanism whereby energy
service providers could lock in long term contracts with large
industrial customers by providing service guarantees based on the
quality of electric power supplied over a period of time. In
return for signing a long term contract, the customer receives
favorable long term rates as well as power quality performance
guarantees from the energy service provider. This assures the
industrial customer that the energy service provider will be
responsive to their problems over the duration of the contract.
Industrial customers are facing increasing energy
costs and increasing competition. Energy service providers are facing
increasing competitive threats from other ESPs in a deregulated
environment. In order for industrial customers to lock in long term
favorable rates and in order for ESPs to prevent customers from going
elsewhere to obtain electric power, the concept of the power quality
contract has emerged. In return for signing a long term contract
whereby the industrial customer agrees to not seek power from other
providers, the Energy Service Provider must guarantee a certain level
of power quality and reliability. If the level of power quality and
reliability is worse than an agreed upon level, the Energy Service
Provider would owe penalty payments to the industrial customer.
Therefore, the incentive exists for the Energy Service Provider to
keep upgrading and improving the performance of the system.
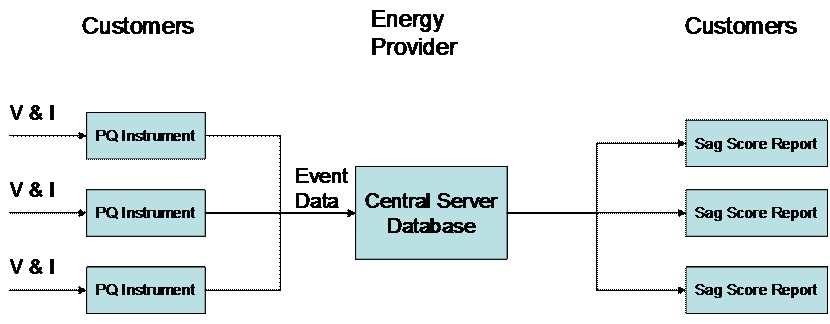
In order to do this, the Energy Service Provider
must install electric power monitoring instrumentation at the service
entrance of each customer. In general these contracts would apply to
large transmission customers where outages are rare, so the primary
concern is the number and severity of voltage sags caused by faults on
the system. These instruments generally must be able to capture RMS
variations, call back to a central server when an event occurs, and be
able to capture enough data such as current to be able to ascertain
whether the event was caused by something on the Energy Service
Provider system or inside the customer facility. This requires
communication from the central server location to the monitoring
instrument either by telephone, Internet, satellite or other.
In general, a database is maintained at the
central server so that event analysis can be conducted as well as the
calculation of a score or index for a particular customer or site. A
base level is required and is generally done before the contract term
is started. The baseline or target is continually updated usually on a
yearly basis and is in effect a rolling average. A score is given for
each event and then totaled on a yearly basis. If the score is above
the target number, then payments are made to the customer based on
previously agreed upon formula.
|
# |
Event |
Name of Process/Activity
|
Description of
Process/Activity |
Information Producer
|
Information
Receiver |
Name of Info Exchanged
|
Additional Notes |
IntelliGrid Architecture Environments |
|
1.1 |
Event Capture and Transmittal |
Event Capture and Transmittal |
If an event is triggered, the instrument calls back to the
central server and the server downloads
the data |
Power Quality Instrument |
Central Server |
Voltage and current waveforms and data |
Basic telecommunication constraints such as modem and dial up
telephone connection, but could also
include internet TCP/IP connectivity or
even cellular |
ESP to Customer |
|
1.2 |
Sag Score Calculated |
Sag Score Calculated |
Based on events recorded, data is characterized and loaded
into a database, then a sag score is
calculated based on previously agreed
algorithm |
Central Server |
Customer |
Data report that includes a sag score |
Data management in terms of culling important information
|
ESP to Customer |
|
1.3 |
Penalty calculation |
|
Based on the previously agreed upon baseline or rolling
average, the previous sag score is
compared to the baseline and a penalty
is then calculated |
Central Server |
Customer |
Report that summarizes penalty payments |
None |
ESP to Customer |