Customer Services - Wind Forecasting Function
Contents
Wind generation is primarily an energy
resource, and cannot dispatched like conventional generation. In
more traditional utility operations, predictions of system load
for the next hour, day, week, etc. are essential for deploying
supply resources such as total costs are minimized while
maintaining system reliability and security. Incremental costs due
to the uncertainty in the timing and quantity of energy delivery
from wind generation facilities in operational time frames can be
reduced with better short-term wind generation forecasts and
appropriate use of those predictions by control area operators and
power markets in scheduling functions and real-time operating
practices.
In situations where resource decisions are made
by according to various market signals, prediction of wind generation
will be important for those who operate the markets and are charged
with responsibility for system security and reliability.
Whether by direct action of an operating entity
or in response to market signals, electric supply resources in an
electric power control area must be managed, scheduled, and operated
to provide for the desired levels of system reliability and security.
Furthermore, to minimize the overall cost of electricity to consumers
in the control area, the supply resources must be deployed in a manner
that leads to the lowest total production cost. Meeting these
objectives and at the same time honoring the myriad constraints on
individual generating units and resulting from contractual obligations
requires the ability to continually assess the present state of the
system and predict probable states hours or days in advance.
Uncertainty in the operational planning time
frame can lead to defensive operating strategies and higher costs.
Wind generation can only increase the uncertainty in the short-term
forecasts utilized to commit and schedule generation, and may lead to
higher operating costs. In real-time operation, additional reserves
might be allocated to cover the uncertainty in the hours-ahead time
frame, again with higher costs.
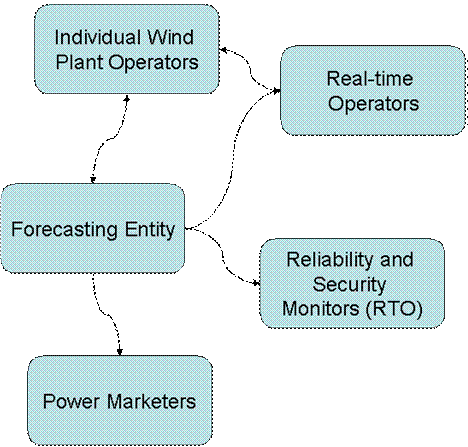
In control areas with multiple wind generation
facilities, forecasts must be generated for each plant on schedules
appropriate for real-time management of the control area as well as
short-term operational planning activities such as unit commitment or
reliability monitoring. Given that the plants in a single control
area are exposed to the same general meteorological conditions, a
wider geographical perspective on wind resource conditions for
forecasting is essential. As a result, the stakeholder groups
involved in wide-area wind generation forecasting are defined as
follows:
-
Operators of the individual wind
plants
-
Control area personnel
responsible for “real-time” operations, i.e. within the hour
and possibly for several hours ahead
-
Control area personnel, which
might include the power marketing functions, responsible for
short-term planning activities, including unit commitment
and scheduling, interchange scheduling, power purchases and
sales, etc.
-
Control area or RTO personnel
responsible for monitoring system security, where generation
dispatch decisions are made for technical reasons related to
system integrity rather than economics
-
A third party that produces
forecasts of wind conditions and possibly wind generation
for plants in the control area.
Individual wind plant operator
-
Provides information on turbine
availability and other plant status indications to
forecasting entity
-
Provides local meteorological
information from plant sensors to forecasting entity
-
Receives plant forecast
information from forecasting entity
Real-time operators
-
Receives wind generation forecast
information from forecasting entity and utilizes for
planning on an hours-ahead basis
-
Receives notification from
individual wind plant operators as to planned changes in
status or availability
-
Notifies individual plant
operators of system conditions that may require certain
actions on the part of the wind generation facility
Power Marketer
Reliability and security monitors (RTO)
Forecasting entity
-
Collects meteorological
information from public and private sensors
-
Executes regional meteorological
model to forecast wind speed for hours and days ahead
-
Collects information from
individual plant operators necessary to forecast production
for plant
-
Collects information from
reliability monitors
-
Develops wind generation forecast
for individual plants and for aggregate wind generation in
control area on the basis of wind plant information and wind
speed forecasts
-
Provides wind generation forecast
to individual wind plant operators, real-time system
operators, power marketers and reliability and security
monitors (RTO)
 |
|
# |
Event |
Name of Process/Activity
|
Description of
Process/Activity |
Information Producer
|
Information
Receiver |
Name of Info Exchanged
|
IntelliGrid Architecture Environments |
|
1.1 |
Provide Data |
Provide Data |
Individual Wind Plant Operator provides information on
turbine availability and local sensor
data to forecasting entity |
Individual Wind Plant Operator |
Forecasting Entity |
Local Data |
Control Center / Corporations |
|
1.2 |
Collect Sensor Data |
Collect Sensor Data |
Forecasting entity collects meteorological data from public
and private sensors |
Sensor Device |
Forecasting Entity |
Sensor Data |
Non-Critical DAC |
|
1.3 |
Make Forecast |
Make Forecast |
Forecasting entity runs models and creates forecast |
Forecasting Entity |
Individual Wind Plant Operators, Power Marketer, Real time
operators, Reliability and Security
Monitors (RTO) |
Wind Generation Forecasts |
Control Center / Corporations |