|
As mentioned in
the introduction to this section, IntelliGrid Architecture project is focused on defining a
set of common modeling elements to create a unified architecture that can be
universally applied to integration of utility components. The diagram below illustrates the elements of
this architecture.
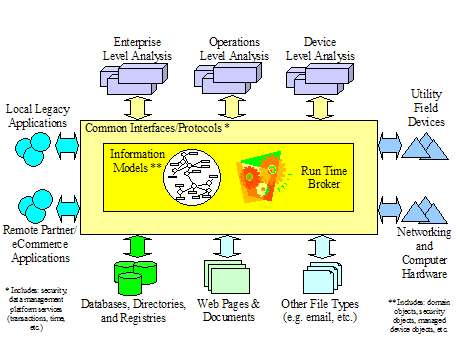
Figure
‑23 Technology Independent Architecture
Figure
23 illustrates at a high level, the required aspects of
IntelliGrid Architecture design. This design is
targeted at meeting all integration for operational and analytic requirements. In this case major functional subsets of a
utility such as devices, applications, databases, and IT resources (networking
and computer hardware) share a common abstract way of communicating with each
other. This common abstraction ensures a
base level of interoperability that can be fully realized via the use of
technology profiles. On top of the
unified architecture, Device Level analysis applications can look across a
seamless collection of utility field devices as well as networking and computing
equipment to uniformly deal with lower level issues of device configuration,
status, documentation, and history.
Operations Level analysis applications enjoy a seamless view of utility
and communication operations. Tactical
business decisions focused on maximizing income and reliability can be made
knowing that all utility information is available and presented in a consistent
manner. Enterprise Level analysis
applications tend to deal with data that has been summarized with key
performance indicators highlights. The
focus here is on longer-term strategic decisions in an attempt to maximize
profitability and minimize risk. It is
imperative that analysis applications provide a concise and unified view of
utility. However, information overload
can only be dealt with a clear vision of what data is available and what
information is needed. The clarity can
only be achieved at a reasonable cost by leveraging the commonality of a
utility embodied in the IntelliGrid Architecture and the standards based approach it
advocates.
|