3.7 Interoperability, DER Interconnection, and Communication Standards and Technologies
3.7.6 Smart Grid Communication Protocol Standards
Communication protocols provide the means to exchange data electronically and can be viewed as electronic languages. Just as there are many different human languages, there are many communication protocols, often developed to meet different types of requirements. Communication protocols also often have a life cycle of being invented, used for a while, and then falling out of favor, typically because the state-of-the-art has developed new capabilities or technologies.
Communication protocols are also usually defined in layers although usually some of the layers can be combined in a particular standard. Common layers (although these too can include sublayers) consist of:
- Information models and profiles, which identify the types of data and their abstract formats, with a focus on the business purpose of the data. For instance, an information model can identify the data elements of “phase A voltage”, “price for energy”, and “customer name”.
- Application layer protocols, which define the message structures (header, body, cyber security parts), services (read, write, get, post, etc.), and translation of the abstract data formats into “bits and bytes”.
- Transport layer protocols, which provide the mechanisms for navigating through networks, such as across the Internet or within a local area network. The most common protocols used are the Internet Protocol (IP) which identifies the address of systems and devices, and the Transport Control Protocol (TCP) which ensures that even long messages that have been cut into pieces (e.g. for efficiency and for sharing the media) are correctly reassembled at the far end. Another common protocol is Ethernet, used primarily on local area networks.
- Media-specific protocols, which are tailored to manage the different characteristics of various media, such as fiber optic cables, microwave systems, WiFi, Bluetooth, etc.
Figure 18 and Figure 19 include some of the more commonly used communication protocols for Smart Grid applications. Of these, the most frequently used by utilities for distribution and DER communications are:
- IEEE 1815 (DNP3) is the communication protocol most North American utilities use for SCADA communications. It does not include an information model
- IEC 61850 is the international information model and protocol for DER and distribution automation. Even when IEC 61850 is not used as the protocol, the IEC 61850 information model forms the basis of other protocols used for communications with DER systems.
- IEEE 2030.5 (SEP2) is a new protocol that was developed for home area networks but may be used for other applications such as utility interactions with DER systems. Its information model is based on IEC 61850.
- OpenADR is another recent protocol, developed explicitly for providing pricing data in demand response applications.
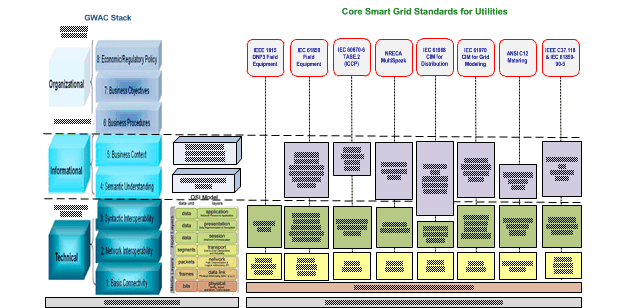
Figure 18 : Smart Grid standards commonly used by utilities
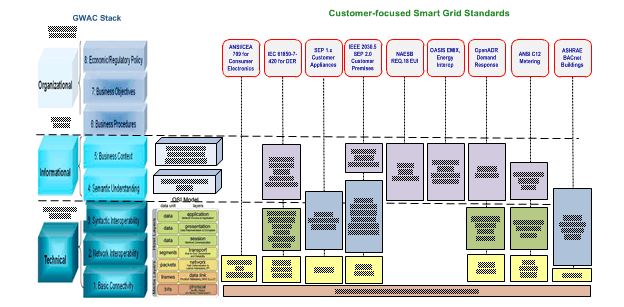
Figure 19 : Smart Grid standards commonly used in customer communications