The Integrated Energy and Communication Systems Architecture
Volume III:
Models
Appendix B:
IntelliGrid Architecture UML/RM-ODP Mapping of Concepts
EPRI Project Manager
Joe Hughes
Cosponsor
Electricity Innovation Institute Consortium for Electric Infrastructure to Support a Digital Society (CEIDS)
EPRI • 3412 Hillview Avenue, Palo Alto, California
94304 • PO Box 10412, Palo Alto, California 94303 • USA
800.313.3774 • 650.855.2121 • askepri@epri.com • www.epri.com
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITIES
THIS DOCUMENT WAS PREPARED BY THE ORGANIZATION(S) NAMED BELOW AS AN ACCOUNT OF WORK SPONSORED OR COSPONSORED BY THE ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, INC. (EPRI). NEITHER EPRI, ANY MEMBER OF EPRI, ANY COSPONSOR, THE ORGANIZATION(S) BELOW, NOR ANY PERSON ACTING ON BEHALF OF ANY OF THEM:
(A) MAKES ANY WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION WHATSOEVER, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, (I) WITH RESPECT TO THE USE OF ANY INFORMATION, APPARATUS, METHOD, PROCESS, OR SIMILAR ITEM DISCLOSED IN THIS DOCUMENT, INCLUDING MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR (II) THAT SUCH USE DOES NOT INFRINGE ON OR INTERFERE WITH PRIVATELY OWNED RIGHTS, INCLUDING ANY PARTY'S INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, OR (III) THAT THIS DOCUMENT IS SUITABLE TO ANY PARTICULAR USER'S CIRCUMSTANCE; OR
(B) ASSUMES RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING ANY CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF EPRI OR ANY EPRI REPRESENTATIVE HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES) RESULTING FROM YOUR SELECTION OR USE OF THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY INFORMATION, APPARATUS, METHOD, PROCESS, OR SIMILAR ITEM DISCLOSED IN THIS DOCUMENT.
ORGANIZATIONS THAT PREPARED THIS DOCUMENT
General Electric Company led by GE Global Research (Prime Contractor)
Significant
Contributions made by
EnerNex Corporation
Hypertek
Lucent Technologies (Partner)
Systems Integration Specialists Company, Inc.
Utility Consulting International (Partner)
ORDERING INFORMATION
Requests for copies of this report should be directed to EPRI Orders and Conferences, 1355 Willow Way, Suite 278, Concord, CA 94520. Toll-free number: 800.313.3774, press 2, or internally x5379; voice: 925.609.9169; fax: 925.609.1310.
Electric Power Research Institute and EPRI are registered service marks of the Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. EPRI. ELECTRIFY THE WORLD is a service mark of the Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © 2002, 2003, 2004 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document describes research sponsored by EPRI and Electricity Innovation Institute.
The publication is a corporate document that should be cited in the literature in the following manner:
THE INTEGRATED ENERGY AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS ARCHITECTURE, EPRI, Palo Alto, CA and Electricity Innovation Institute, Palo Alto, CA: 2003 {Product ID Number.
One of the charters of IntelliGrid Architecture is to use a rigorous standardized modeling methodology. The IntelliGrid Architecture team selected the Reference Model for Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) {TU-T Rec. X.901 | ISO/IEC 10746-1 to ITU-T Rec. X.904 | ISO/IEC 10746-4} to provide the methodology for the development of an architecture framework which will support distributed processing in heterogeneous environments.
By design RM-ODP does not prescribe any notational constructs for rendering the architecture in accordance with the methodology. Thus, the team selected the Unified Modeling Language (UML) as the notational construct for the architecture.
Since the methodology and the notational constructs are not shared, the project needs to define the mapping between the RM-ODP concepts and the corresponding UML notational constructs. The IntelliGrid Architecture team was able to leverage bodies of work put forth by OMG, EDF and others in this area; however, more work is needed in the standards community to complete this mapping.
The remainder of this document outlines most of the RM-ODP concepts, and attempts to clearly define the mapping between the RM-ODP concept and the corresponding UML notational construct. Where possible, an example is provided for clarity. It should be noted that there are a substantial portion of RM-ODP concepts that are not mapped into UML notation. The team developed the mapping as the RM-ODP concept was encountered in the architecture framework development. As the architecture framework continues to develop, additional RM-ODP concepts will need explicit mapping into the corresponding UML notational constructs.
Appendix
B –IntelliGrid Architecture UML/RM-ODP Mapping of Concepts
Actor
(with respect to an action)
Artifact
(with respect to an action)
Computational
interface template
Consumer
object (with respect to a communication)
Contracting
party (with respect to a contract)
Engineering
interface reference
Engineering
interface reference management domain
Engineering
interface reference management policy
Field of
Application (of a specification)
Initiating
object (with respect to a communication)
Instantiation
(of an <X> Template)
Producer
object (with respect to a communication)
Index of RM-ODP Mapping of Concepts
Mapping of UML and
RM-ODP
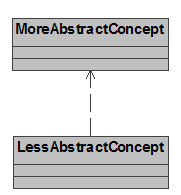
Abstraction
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.3
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: Abstraction
ODP-Definition: The
process of suppressing irrelevant detail to establish a simplified model, or
the result of that process.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.5.2.1
UML-Mapping: Abstraction
corresponds to a UML Dependency association using the predefined stereotype
Abstraction association.
Example:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.1
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Access transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency that masks differences in data representation and invocation
mechanisms to enable inter-working between objects.
Status: Unmapped.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.3
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Action
ODP-Definition: Something
which happens. An action occurrence. The set of actions associated with an
object is partitioned into internal actions and interactions.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.63
UML-Mapping: An
action corresponds to a UML Message bound to an operation that specifies
communication between two instances.
Note this is a refinement of a Step.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.5
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Activity
ODP-Definition: A
single-headed directed acyclic graph of actions, where occurrence
of each action in the graph is made possible by the occurrence of all
immediately preceding actions (i.e. by all adjacent actions which
are closer to the head).
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.65
UML-Mapping: Activity
corresponds to a UML Collaboration diagram.
Example:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.1
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Actor (with respect to an action)
ODP-Definition: An enterprise
object that participates in
the action.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.65
UML-Mapping: An ODP Actor corresponds to a UML Actor
Example:

ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.7
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Agent
ODP-Definition: An enterprise object that has been delegated
(authority, responsibility, a function, etc.) by and acts for another
enterprise object (in
exercising the authority, carrying out the responsibility, performing the
function, etc.).
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.3
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Announcement
ODP-Definition: An
interaction -- the invocation -- initiated by a client object
resulting in the conveyance of information from that client object to a server
object, requesting a function to be performed by that server object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.1
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Application management
ODP-Definition: The
management of applications within an ODP system. Some aspects of applications
management are common to all applications and are termed application
independent management. Those aspects that are specific to a given application
are termed application specific management.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.6
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: Architecture (of a system)
ODP-Definition: A
set of rules to define the structure of a system and the
interrelationships between its parts.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Artifact (with respect to an action)
ODP-Definition: An enterprise
object that is referenced
in the action.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.5.2.2
UML-Mapping: An ODP Artifact corresponds to a UML
Artifact
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.4
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: Atomicity
ODP-Definition: An
entity is atomic at a given level of abstraction if it cannot be
subdivided at that level of abstraction.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.4.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Policy Concepts
ODP-Concept: Authorization
ODP-Definition: A prescription that a
particular behavior must not be prevented.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.1
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Basic engineering object
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object that requires the support of a distributed
infrastructure.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.6
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Behavior (of an object)
ODP-Definition: A
collection of actions with a set of constraints on when they may occur.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.4
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Behavioral compatibility
ODP-Definition: An
object is behaviorally compatible with a second object with
respect to a set of criteria if the first object can replace the second
object without the environment being able to notice the difference in
the objects’ behavior on the basis of the set of criteria.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.10
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Binder
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object in a channel, which maintains a distributed binding
between interacting basic engineering objects.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.4.2
ODP-Category: Establishing
Behaviors
ODP-Concept: Binding
ODP-Definition: A contractual
context, resulting from a given establishing behavior.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.4.1
ODP-Category: Establishing
Behaviors
ODP-Concept: Binding Behavior
ODP-Definition: An
establishing behavior between two or more interfaces (and hence
between their supporting objects). "To bind" means "to
execute a binding behavior".
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.15
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Binding endpoint identifier
ODP-Definition: An
identifier, in the naming context of a capsule, used by a basic
engineering object to select one of the bindings in which it is
involved, for the purpose of interaction.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.14
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Binding object
ODP-Definition: A computational
object which supports a binding between a set of other computational
objects.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
Example:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.4.3
ODP-Category: Establishing
Behaviors
ODP-Concept: Binding precondition
ODP-Definition: A
set of conditions required for the successful execution of a binding
behavior.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.4
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Capsule
ODP-Definition: A configuration
of engineering objects forming a single unit for the purpose of
encapsulation of processing and storage.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.5
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Capsule manager
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object that manages the engineering objects in a capsule.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.1
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Chain (of actions)
ODP-Definition: A
sequence of actions within an activity where, for each adjacent
pair of actions, occurrence of the first action is necessary for
the occurrence of the second action.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.10.4.2
UML-Mapping: UML
correspondence rule: An ODP chain of actions is modeled as a UML
interaction. The numbering of the
sequence steps conveys the order and concurrency and iteration of the steps
occur. Using a Dewey Decimal scheme,
each level of nested procedure call is separated by a dot ‘.’. Within a level,
the sequence number comprises an optional letter and an integer number. The
letter specifies a concurrent sequence within the next higher level; all letter
sequences are concurrent with other letter sequences. The number specifies the sequencing of
messages in a given letter sequence. The absence of a letter is treated as a
default 'main sequence' in parallel with the lettered sequences.
Example:
Chain of Actions 1:
1.1 - Do step 1
1.2A.1 - In parallel to activity 2 B do step 1
1.2A.2 - In
parallel to activity 2 B do step 2
1.2B.1 - In
parallel to activity 2 A do step 1
1.2B.2 - In
parallel to activity 2 A do step 2
1.3 - Do step 3
1.3.1 - nested step 3.1
1.3.2 - nested step 3.2
Chain of Actions 2:
2.1 - Do step 1
2.2 – Do step 2
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.8
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Channel
ODP-Definition: A configuration
of stubs, binders, protocol objects and interceptors
providing a binding between a set of interfaces to basic
engineering objects, through which interaction can occur.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.20
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Checkpoint
ODP-Definition: An
object template derived from the state and structure of an engineering
object that can be used to instantiate another engineering object,
consistent with the state of the original object at the time of check
pointing.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.21
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Check-pointing
ODP-Definition: Creating
a checkpoint. Checkpoints can only be created when the engineering
object involved satisfies a pre-condition stated in a check-pointing
policy.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.8
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Class (of <X>s)
ODP-Definition: The
set of all <X>s satisfying a type. The elements of the set are
referred to as members of the class.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.5
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Client object
ODP-Definition: An
object which requests that a function be performed by another object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.24
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Cloning
ODP-Definition: Instantiating
a cluster from a cluster checkpoint.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.2
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Cluster
ODP-Definition: A configuration
of basic engineering objects forming a single unit for the purposes of deactivation,
check pointing, reactivation, recovery and
migration.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.22
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Cluster checkpoint
ODP-Definition: A cluster
template containing checkpoints of the basic engineering objects
in a cluster.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.3
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Cluster manager
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object that manages the basic engineering objects in a
cluster.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.19
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Cluster template
ODP-Definition: An
object template for a configuration of objects and any activity
required to instantiate those objects and establish initial bindings.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Commitment
ODP-Definition: An action resulting
in an obligation by one or more of the participants in the act to comply
with a rule or perform a contract.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.8
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Communication
ODP-Definition: The
conveyance of information between two or more objects as a result of one
or more interactions, possibly involving some intermediate objects.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.14
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Communication interface
ODP-Definition: An
interface of a protocol object that can be bound to an interface
of either an interceptor object or another protocol object at an inter-working
reference point.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.2
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Communication management
ODP-Definition: Management
of objects which support the communication between objects
within an ODP system.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.13
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Communications domain
ODP-Definition: A
set of protocol objects capable of inter-working.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.5.1.1
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Language
ODP-Concept: Community
ODP-Definition: A configuration
of objects formed to meet an objective. The objective is expressed as a contract
that specifies how the objective can be met.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.66
UML-Mapping: UML defines collaboration as an abstract
structure concept. The members of the
collaboration represent cooperative elements that come together to meet a
specific objective.
Example:

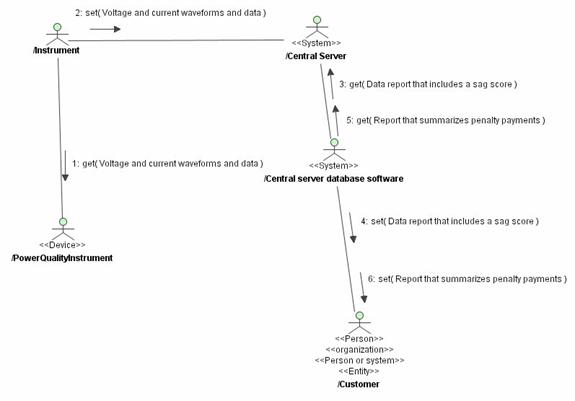
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.2.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Community
ODP-Concept: Community object
ODP-Definition: A composite enterprise object that represents a community.
Components of a community object are
objects of the community represented.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.66
UML-Mapping: Owned elements of the collaboration.
Example:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.1(b)
ODP-Category: ODP
Conformance
ODP-Concept: Compliance
ODP-Definition: Adherence
to requirements for the necessary consistency of one member of the family of
ODP standards with another (such as the RM-ODP). Compliance is established
during the standardization process. If a specification is compliant, directly
or indirectly, with some other standards then the propositions that are
true in those standards are also true in a conformant implementation
of the specification.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.2
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Composite object
ODP-Definition: An
object expressed as a composition.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.1(a)
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Composition (of objects)
ODP-Definition: A
combination of two or more objects yielding a new object, at a
different level of abstraction.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.1(b)
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Composition (of behaviors)
ODP-Definition: A
combination of two or more behaviors yielding a new behavior.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.10
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Computational interface template
ODP-Definition: An
interface template for either a signal interface, a stream
interface or an operation interface. A computational interface
template comprises a signal, a stream or an operation
interface signature as appropriate, a behavior specification and an environment
contract specification.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.9
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Computational object template
ODP-Definition: An
object template which comprises a set of computational interface
templates which the object can instantiate, a behavior
specification and an environment contract specification.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.1.1.3
ODP-Category: Viewpoint
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Computational viewpoint
ODP-Definition: A viewpoint
on an ODP system and its environment which enables distribution through
functional decomposition of the system into objects which interact at
interfaces.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: The
computational viewpoint is primarily represented as class diagrams showing the
interface definitions and the collaboration, sequence and activity diagrams
showing the object flows.
Example:
 :
:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.2
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Configuration
ODP-Definition: A
collection of objects able to interact at interfaces. A
configuration determines the set of objects involved in each
interaction.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.1(a)
ODP-Category: ODP
Conformance
ODP-Concept: Conformance
ODP-Definition: Conformance
relates an implementation to a standard. Any proposition that is true in the
specification must be true in its implementation.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.7
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Conformance point
ODP-Definition: A reference
point at which behavior may be observed for the purposes of
conformance testing.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.4
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Consumer object (with respect to a
communication)
ODP-Definition: An
object that is a sink of the information conveyed.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.63
UML-Mapping: A
producer object is on the supplier side of a UML Message that specifies
communication between two instances.
Example:


ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.1
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Contract
ODP-Definition: An
agreement governing part of the collective behavior of a set of objects.
A contract specifies obligations, permissions
and prohibitions for the objects involved.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
UML-Model:
Example:
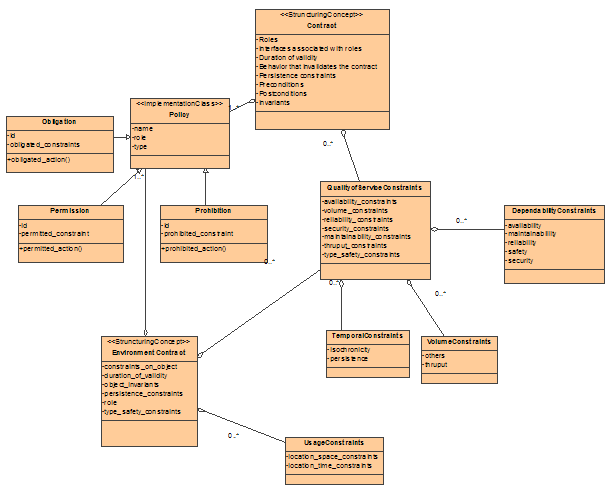
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.7
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Contracting party (with respect to a
contract)
ODP-Definition: A party
that agrees to that contract.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.2.3
ODP-Category: Contractual
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Contractual context
ODP-Definition: The
knowledge that a particular contract is in place, and thus that a
particular behavior of a set of objects is required.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.15
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Creation (of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: Instantiating
an <X>, when it is achieved by an action of objects in the
model. <X> can be anything that can be instantiated, in particular objects and interfaces.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.23
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Deactivation
ODP-Definition: Check-pointing a cluster, followed by deletion of the cluster.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.3
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Declaration
ODP-Definition: An action that
establishes a state of affairs in the environment of the object making the declaration.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.3(b)
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Decomposition (of a behavior)
ODP-Definition: The
specification of a given behavior as a composition.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.3(a)
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Decomposition (of an object)
ODP-Definition: The
specification of a given object as a composition.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.4
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Delegation
ODP-Definition: The action
that assigns authority, responsibility or a function to another object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.17
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Deletion (of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: The
action of destroying an instantiated <X>. <X> can be
anything that can be instantiated, in particular objects
and interfaces.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.21
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Derived class/ Base class
ODP-Definition: If
a template A is an incremental modification of a template B, then
the template class CA of instances of A is a derived class
of the template class CB of instances of B, and the CB is
a base class of CA.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.1
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Distribution transparency
ODP-Definition: The
property of hiding from a particular user the potential behavior of some
parts of a distributed system.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.4
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Dividing action
ODP-Definition: An
action which enables two or more chains.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.3
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: <X> Domain
ODP-Definition: A
set of objects, each of which is related by a characterizing
relationship <X> to a controlling object.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: An ODP domain is modeled as a package in
UML having the stereotype of <<domain>>.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-3.6.1.3
ODP-Category: Information
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Dynamic schema
ODP-Definition: A
specification of the allowable state changes of one or more information
objects, subject to the constraints of any invariant schemata.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.2.2
ODP-Category: Contractual
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Enabled behavior
ODP-Definition: The
behavior characterizing a set of objects which becomes possible
as a result of establishing behavior.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.16
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Engineering interface reference
ODP-Definition: An
identifier, in the context of an engineering interface reference
management domain, for an engineering object interface that is
available for distributed binding.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.17
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Engineering interface reference
management domain
ODP-Definition: A
set of nodes forming a naming domain for the purpose of assigning
engineering interface references.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.18
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Engineering interface reference
management policy
ODP-Definition: A
set of permissions and prohibitions that govern the federation
of engineering interface reference management domains.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.1.1.4
ODP-Category: Viewpoint
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Engineering viewpoint
ODP-Definition: A viewpoint
on an ODP system and its environment that focuses on the mechanisms and
functions required to support distributed interaction between objects in the
system.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.1.1.1
ODP-Category: Viewpoint
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Enterprise viewpoint
ODP-Definition: A viewpoint
on an ODP system and its environment that focuses on the purpose, scope and policies for that system.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.54
UML-Mapping: Enterprise
viewpoint represents the purpose, scope and policies
of the system and is primarily modeled with use case diagrams and class
diagrams.
Example:
Use Case:
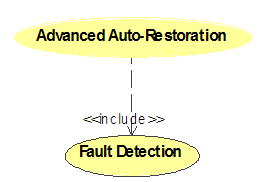
As shown in the Use
Case Diagram, “Advanced Auto-Restoration” is an IntelliGrid Architecture enterprise activity that
includes “Fault Detection” service. The two use cases are linked through a
“<<include>>” dependency.
The class diagram is
used to expose the contractual bindings of the actors.
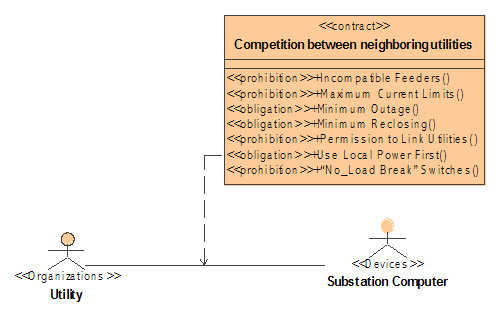
As shown in the
figure, the two actors are associated with each other with a contract called
“Competition between neighboring utilities” binding the interface. The UML
“permission” association shows the binding.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.1
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: Entity
ODP-Definition: Any
concrete or abstract thing of interest.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: An
ODP Entity is modeled as any one of UML’s Modeling
Elements.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.2
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Environment (of an object)
ODP-Definition: The
part of the model which is not part of that object.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.66
UML-Mapping: UML defines
collaboration as an abstract structure concept.
The members of the collaboration represent cooperative elements that
come together to meet a specific objective.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.3
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Environment contract
ODP-Definition: A
contract between an object and its environment, including quality of service
constraints, usage and management constraints.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: Association
<<environmentContract>>
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.5
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Epoch
ODP-Definition: A
period of time for which an object displays a particular behavior.
Any one object is in a single epoch at one time, but interacting objects
may be in different epochs at the time of interaction.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.5.2
ODP-Category: Dependability
ODP-Concept: Error
ODP-Definition: Part
of an object state which is liable to lead to failures. A
manifestation of a fault in an object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.2.1
ODP-Category: Contractual
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Establishing behavior
ODP-Definition: The
behavior by which a given contract is put in place between given objects.
An establishing behavior can be a) explicit, resulting from the interactions of
objects that will take part in the contract; or b) implicit,
being performed by an external agency (e.g. a third party object, not
taking part in the contract) or having been performed in a previous epoch.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.5
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Evaluation
ODP-Definition: An action
that assesses the value of something.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.5.1
ODP-Category: Dependability
ODP-Concept: Failure
ODP-Definition: Violation
of a contract.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.2
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Failure transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks, from an object, the failure and possible
recovery of other objects (or itself), to enable fault tolerance.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.5.3
ODP-Category: Dependability
ODP-Concept: Fault
ODP-Definition: A
situation that may cause errors to occur in an object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.5.1.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Language
ODP-Concept: <X> Federation
ODP-Definition: A community
of <x> domains.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.1.2
ODP-Category: Enterprise
System
ODP-Concept: Field of Application (of a
specification)
ODP-Definition: The
properties the environment of the ODP system must have for the
Specification of that system to be used.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.5
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Flow
ODP-Definition: An
abstraction of a sequence of interactions, resulting in conveyance of
information from a producer object to a consumer object. A flow may be used to abstract over, for
example, the exact structure of a sequence of interactions, or over a
continuous interaction including the special case of an analogue information
flow.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.90
UML-Mapping: ODP
Flow corresponds to UML Action Object Flow conveyed in a UML Collaboration
Diagram. Flow is also related to the UML
Collaboration diagram showing the Actors involved as the producer and consumer
objects.
Example:
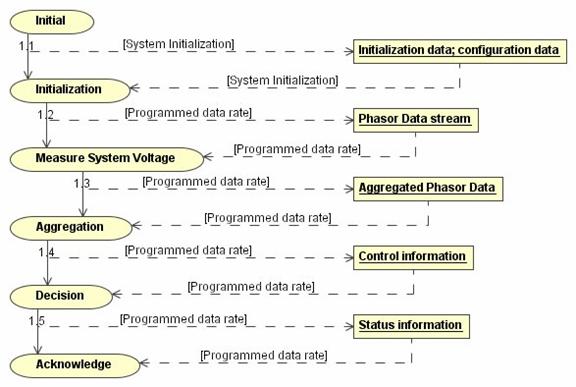
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.5
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Forking action
ODP-Definition: A dividing
action, where the enabled chains must (subject to failure)
eventually join each other, i.e. the enabled chains cannot join other chains
and they cannot terminate separately.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Mapping: See
Chain of Action.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.1
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: <X> Group
ODP-Definition: A
set of objects with a particular characterizing relationship <X>.
The relationship <X> characterizes either the structural relationship
among objects or an expected common behavior of the objects.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.7
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Head action
ODP-Definition: In
a given activity, an action that has no predecessor.
Status: Mapped.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.65
UML-Mapping: The Head
Action is the First Action in a UML Collaboration diagram.
Example:


ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.2
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Identifier
ODP-Definition: An
unambiguous name, in a given naming context.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.9.1.1
ODP-Category: Technology
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Implementable standard
ODP-Definition: A template
for a technology object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.9.1.2
ODP-Category: Technology
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Implementation
ODP-Definition: A
process of instantiation whose validity can be subject to test.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.1.1.2
ODP-Category: Viewpoint
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Information viewpoint
ODP-Definition: A viewpoint
on an ODP system and its environment that focuses on the semantics of
information and information processing.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: The
information viewpoint is primarily mapped to class diagrams showing the data
model – and state diagrams depicting the different states the objects can be
in.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.1
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Initiating object (with respect to a
communication)
ODP-Definition: An
object causing a communication.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.63
UML-Mapping: An
ODP initiating object corresponds to a UML Object corresponding to the supplier
side of a Message / Stimulus
Example:


ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.18
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Instance
ODP-Definition: An
<X> that satisfies the type.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.13
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Instantiation (of an <X>
Template)
ODP-Definition: An
<X> produced from a given <X> template and other necessary
information. This <X> exhibits the features specified in the <X> template.
<X> can be anything that has a type.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.11
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Interaction point
ODP-Definition: A
location at which there exists a set of interfaces.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.11
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: <X> interceptor
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object in a channel, placed at a boundary between
<x> domains. An <x> interceptor performs checks to enforce
or monitor policies on permitted interactions between basic engineering
objects in different domains; performs transformations to mask
differences in interpretation of data by basic engineering objects in
different domains.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.3.4
ODP-Category: Classes
of Reference Points
ODP-Concept: Interchange reference point
ODP-Definition: A reference
point at which an external physical storage medium can be introduced into
the system. An interchange conformance requirement is stated in terms of the behavior
(access methods and formats) of some physical medium so that information can be
recorded on one system and then physically transferred, directly or indirectly,
to be used on another system.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.4
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Interface
ODP-Definition: An
abstraction of the behavior of an object that consists of a
subset of the interactions of those object together with a set of constraints
on when they may occur.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.29
UML-Mapping: An
ODP interface type is modeled as a UML interface.
Example:
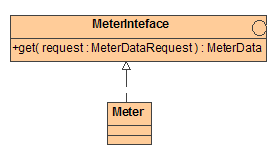
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.4
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Interface role
ODP-Definition: A role of a community
identifying behavior which takes place with the participation of objects that
are not a members of that community.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.12
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Interface signature
ODP-Definition: The
set of action templates associated with the interactions of an
interface.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.4
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Interrogation
ODP-Definition: An
interaction consisting of one interaction -- the invocation -- initiated
by a client object, resulting in the conveyance of information from that
client object to a server object, requesting a function to be
performed by the server object, followed by a second interaction -- the termination
-- initiated by the server object, resulting in the conveyance of
information from the server object to the client object in
response to the invocation.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.3.3
ODP-Category: Classes
of Reference Points
ODP-Concept: Inter-working reference point
ODP-Definition: A reference
point at which an interface can be established to allow communication
between two or more systems. An inter-working conformance requirement is stated
in terms of the exchange of information between two or more systems.
Inter-working conformance involves interconnection of reference points.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.16
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Introduction (of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: Instantiating
an <X> when it is not achieved by an action of objects in
the model.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.22
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Invariant
ODP-Definition: A
predicate that a specification requires being true for the entire lifetime of a
set of objects.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.6.1.1
ODP-Category: Information
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Invariant schema
ODP-Definition: A
set of predicates on one or more information objects that must always be
true. The predicates constrain the possible states and state changes of
the objects to which they apply.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.85
UML-Mapping: Guard
condition is one of the predicates that constrain state changes..
Example: These
Guard conditions can be seen in Activity diagrams


ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.3.2
ODP-Category: Temporal
Properties
ODP-Concept: Isochronicity
ODP-Definition: A
sequence of actions is isochronous if every adjacent pair of actions in
the sequence occupies unique, equally sized, adjacent intervals in time.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.9.1.3
ODP-Category: Technology
Concepts
ODP-Concept: IXIT
ODP-Definition: Implementation eXtra Information for
Testing.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.3
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Joining action
ODP-Definition: An
action shared between two or more chains resulting in a single chain.
UML-Mapping: See
Chain of Action.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.2.4
ODP-Category: Contractual
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Liaison
ODP-Definition: The
relationship between a set of objects which results from the performance
of some establishing behavior; the state of having a contractual
context in common.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.9
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Location in space
ODP-Definition: An
interval of arbitrary size in space at which an action can occur.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.10
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Location in time
ODP-Definition: An
interval of arbitrary size in time at which an action can occur.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.3
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Location transparence
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks the use of information about location in space
when identifying and binding to interfaces.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.4
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Managed role
ODP-Definition: The
view of the management interface of an object that is being
managed within an ODP system.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.3
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Management information
ODP-Definition: Knowledge
concerning objects which are of relevance to management.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.5
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Managing role
ODP-Definition: The
view of an object which is performing managing actions.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.27
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Migration
ODP-Definition: Moving
a cluster to a different capsule.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.4
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Migration transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks, from an object, the ability of a system to
change the location of that object. Migration is often used to achieve
load balancing and reduce latency.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.1
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Name
ODP-Definition: A term
which, in a given naming context, refers to an entity.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.7
UML-Mapping: An
ODP Name corresponds to a UML name that identifies a model element uniquely
within a given scope.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.8
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Name resolution
ODP-Definition: The
process by which, given an initial name and an initial naming context,
an association between a name and the entity designated by the
initial name can be found.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.3
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Name space
ODP-Definition: A
set of terms usable as names.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.13
UML-Mapping: An
ODP Name space corresponds to a UML Package.
Owned elements of a package must be named uniquely.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.5
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Naming action
ODP-Definition: An
action that associates a term from a name space with a
given entity.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.4
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Naming context
ODP-Definition: A
relation between a set of names and a set of entities. The set of
names belongs to a single name space.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.6
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Naming domain
ODP-Definition: A
subset of a naming context such that all naming actions are
performed by the controlling object of the domain (the name
authority object).
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.12.4.7
ODP-Category: Naming
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Naming graph
ODP-Definition: A
directed graph where each vertex denotes a naming context, and where
each edge denotes an association between a name appearing in the naming
context, and the target-naming context.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.7
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Node
ODP-Definition: A configuration
of engineering objects forming a single unit for the purpose of location
in space, and which embodies a set of processing, storage and communication
functions.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.14.6
ODP-Category: Management
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Notification
ODP-Definition: An
interaction initiated by an object operating in a managed role.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.6
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Nucleus
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object that coordinates processing, storage and communications
functions for use by other engineering objects within the node to which it
belongs.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
Example:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.1
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: Object
ODP-Definition: A model
of an entity. An object interacts with its environment at its interaction
points.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: An
ODP object is modeled as a UML object.
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.2.1
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Community
ODP-Concept: Objective
ODP-Definition: Practical advantage or
intended effect, expressed as preferences about future states.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.4
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
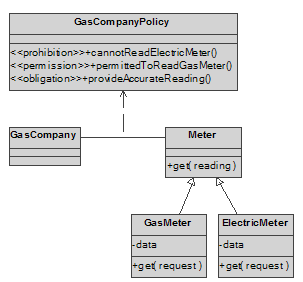
ODP-Concept: Obligation
ODP-Definition: A
prescription that a particular behavior is required. An obligation is
fulfilled by the occurrence of the prescribed behavior.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.5.2.15
UML-Mapping: Obligation
is modeled in UML as a directed Dependency relationship using the stereotyped
<<permission>> that is predefined by the UML specification. The Dependency association extends from the
Policy or Operations reflecting the obligation (supplier element – or arrow
head) to the element affected by the obligation (client – or arrow tail). The operation defined in the policy
reflecting the operation shall be stereotyped as <<obligation>>.
Example: The figure
illustrates a policy between a gas company and a meter, where the gas company
is permitted to read the gas meter, but prohibited from reading the electric
meter.
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.2
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Operation
ODP-Definition: An
interaction between a client object and a server object which is
either an interrogation or an announcement.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference: 2.36
UML-Mapping: An
ODP operation corresponds to a UML Operation
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.7
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Operation interface
ODP-Definition: An
interface in which all the interactions are operations.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.12
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Operation interface signature
ODP-Definition: An
interface signature for an operation interface. An operation
interface signature comprises a set of announcement and interrogation
signatures as appropriate, one for each operation type in the interface,
together with an indication of causality (client or server, but not both) for
the interface as a whole, with respect to the object which instantiates the template.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.1
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Party
ODP-Definition: An enterprise object modeling a natural person
or any other entity considered to have some of the rights, powers and duties of a natural person.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.3.2
ODP-Category: Classes
of Reference Points
ODP-Concept: Perceptual reference point
ODP-Definition: A
reference point at which there is some interaction between the system and the
physical world.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.5
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Permission
ODP-Definition: A
prescription that a particular behavior is allowed to occur. Permission is equivalent to there being no obligation
for the behavior not to occur.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.5.2.15
UML-Mapping: Permission is modeled in UML as a
directed Dependency relationship using the stereotyped
<<permission>> that is predefined by the UML specification. The Dependency association extends from the
Policy or Operations reflecting the permission (supplier element – or arrow
head) to the element affected by the permission (client – or arrow tail). The operation defined in the policy
reflecting the operation shall be stereotyped as <<permission>>.
Example: The figure
illustrates a policy between a gas company and a meter, where the gas company
is permitted to read the gas meter, but prohibited from reading the electric
meter.

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.3.1
ODP-Category: Temporal
Properties
ODP-Concept: Persistence
ODP-Definition: The
property that an object continues to exist across changes of contractual
context or of epoch.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.7
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Persistence transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks, from an object, the deactivation
and reactivation of other objects (or itself). Deactivation and reactivation
are often used to maintain the persistence of an object when a system is
unable to provide it with processing, storage and communication functions
continuously.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.7
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
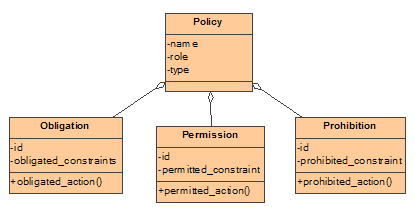
ODP-Concept: Policy
ODP-Definition: A
set of rules related to a particular purpose. A rule can be expressed as an obligation,
permission or a prohibition.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Model:
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: The IntelliGrid Architecture Team has concluded a way to characterize RM-ODP policies in a verifiable
manner is to represent the policy as a classifier having stereotyped operations
corresponding to <<prohibitions>>, <<permissions>> and
<<obligations>>. The policy is associated with the associations,
operations, classifiers, actors or interfaces using a
Dependency relationship. The Dependency association extends from clients or
entities to the Policy or supplier affecting the entity.
Example: The figure
illustrates a policy between a gas company and a meter, where the gas company
is permitted to read the gas meter, but prohibited from reading the electric
meter.

ODP-Reference: -
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Post-condition
ODP-Definition: A
predicate that a specification requires to be true immediately after the
occurrence of an action.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.16
UML-Mapping: An
ODP Post-Condition corresponds to a UML constraint.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.23
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Precondition
ODP-Definition: A
predicate that a specification requires to be true for an action to
occur.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.16
UML-Mapping: An
ODP Pre-Condition corresponds to a UML constraint.
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.6
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Prescription
ODP-Definition: An
act that establishes a rule.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.5.7
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Accountability Concepts
ODP-Concept: Principal
ODP-Definition: A party
that has delegated (authority, a function, etc.) to another.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.5
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Process
ODP-Definition: A collection of steps
taking place in a prescribed manner and leading to an objective.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.65
UML-Mapping: Process
corresponds to a UML Collaboration diagram.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.3
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Producer object (with respect to a
communication)
ODP-Definition: An
object that is the source of the information conveyed.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.63
UML-Mapping: A
producer object is on the supplier side of a UML Message that specifies
communication between two instances.
Example:


ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.3.1
ODP-Category: Classes
of Reference Points
ODP-Concept: Programmatic reference point
ODP-Definition: A
reference point at which a programmatic interface can be established
to allow access to a function. A programmatic conformance requirement is
stated in terms of a behavioral compatibility with the intent that one object
be replaced by another. A programmatic interface is an interface
that is realized through a programming language binding.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.6
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Prohibition
ODP-Definition: A
prescription that a particular behavior must not occur. A prohibition is
equivalent to there being an obligation for the behavior not to
occur.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.5.2.15
UML-Mapping: Prohibition
is modeled in UML as a directed Dependency relationship using the stereotyped
<<permission>> that is predefined by the UML specification. The Dependency association extends from the
Policy or Operations reflecting the prohibition (supplier element – or arrow
head) to the element affected by the prohibition (client – or arrow tail). The operation defined in the policy
reflecting the operation shall be stereotyped as <<prohibition>>.
Example: The figure
illustrates a policy between a gas company and a meter, where the gas company
is permitted to read the gas meter, but prohibited from reading the electric
meter.

ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.2
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: Proposition
ODP-Definition: An
observable fact or state of affairs involving one or more entities, of
which it is possible to assert or deny that it holds for those entities.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.12
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Protocol object
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object in a channel, which communicates with other
protocol objects in the same channel to achieve interaction between basic
engineering objects (possibly in different clusters, possibly in
different capsules, possibly in different nodes).
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.11.2.2
ODP-Category: Policy
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Quality of Service
ODP-Definition: A
set of quality requirements on the collective behavior of one or more objects.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.6.2.5
UML-Mapping: Quality of Service corresponds to UML
Tagged Values representing the collective requirements for the collective
behavior of the identified object.
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.26
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Reactivation
ODP-Definition: Cloning a cluster following its deactivation.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.25
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Recovery
ODP-Definition: Cloning a cluster after cluster failure
or deletion.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.6
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Reference point
ODP-Definition: An
interaction point defined in an architecture for selection as a conformance
point in a specification that is compliant with that architecture.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.5
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Refinement
ODP-Definition: The
process of transforming one specification into a more detailed specification.
Specifications and their refinements typically do not coexist in the same
system description.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.5
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Relocation transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks relocation of an interface from other interfaces
bound to it.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.6
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Replication transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks the use of a group of mutually behaviorally
compatible objects to support an interface. Replication is often
used to enhance performance and availability.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.3
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Resource
ODP-Definition: An enterprise object which is essential to some behavior
and which requires allocation or may become unavailable.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.2
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Responding object
ODP-Definition: An
object taking part in a communication, which is not the initiating
object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.14
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
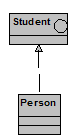
ODP-Concept: Role
ODP-Definition: Identifier
for a behavior, which may appear as a parameter in a template for
a composite object, and which is associated with one of the component objects
of the composite object.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.29.2
UML-Mapping: Role
as an Interface, where a role represents a behavioral concept instead of an
identifier.
Example: The role
of Student is modeled as a UML interface that is assumed by the class Person.
The association of Person to Student corresponds to a UML Realization
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.1.1
ODP-Category: Enterprise
System
ODP-Concept: Scope
(of a system)
ODP-Definition: The
behavior that system is expected to exhibit.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.7.2
ODP-Category: Basic
Linguistic Concepts
ODP-Concept: Sentence
ODP-Definition: A
linguistic construct containing one or more terms and predicates; a
sentence may be used to express a proposition about the entities
to which the terms refer.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.3.6
ODP-Category: Causality
ODP-Concept: Server object
ODP-Definition: An
object which performs some function on behalf of a client object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.1
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Signal
ODP-Definition: An
atomic shared action resulting in one-way communication from an
initiating object to a responding object.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.6
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Signal interface
ODP-Definition: An
interface in which all the interactions are signals.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.11
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Signal interface signature
ODP-Definition: An
interface signature for a signal interface. A signal interface
signature comprises a finite set of action templates, one for each signal
type in the interface. Each action template comprises the name
for the signal, the number, names and types
of its parameters and an indication of causality (initiating or responding,
but not both) with respect to the object which instantiates the template.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.6
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Spawn action
ODP-Definition: A dividing
action, where the enabled chains will not join. The enabled chains
may interact and they may terminate separately.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.5.4
ODP-Category: Dependability
ODP-Concept: Stability
ODP-Definition: The
property that an object has with respect to a given failure mode
if it cannot exhibit that failure mode.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.8.7
ODP-Category: Basic
Modeling Concepts
ODP-Concept: State (of an object)
ODP-Definition: At
a given instant in time, the condition of an object that determines the
set of all sequences of actions in which the object can take
part.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.75
UML-Mapping: An
ODP State corresponds to a UML State
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.6.1.2
ODP-Category: Information
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Static schema
ODP-Definition: A
specification of the state of one or more information objects, at
some point in time, subject to the constraints of any invariant schemata.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.3.6
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Step
ODP-Definition: An abstraction of an action,
used in a process, that may leave unspecified objects that
participate in that action.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 3.63
UML-Mapping: An
step corresponds to a UML Message that specifies communication between two
instances.
Example:

ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.8
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Stream interface
ODP-Definition: An
interface in which all the interactions are flows.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.7.1.13
ODP-Category: Computational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Stream interface signature
ODP-Definition: An
interface signature for a stream interface. A stream interface
comprises a finite set of action templates, one for each flow type
in the stream interface. Each action template for a flow
contains the name of the flow, the information type of the flow,
and an indication of causality for the flow (i.e., producer or consumer
but not both) with respect to the object which instantiates the template.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.8.1.9
ODP-Category: Engineering
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Stub
ODP-Definition: An
engineering object in a channel, which interprets the
interactions conveyed by the channel, and performs any necessary
transformation or monitoring based on this interpretation.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.8
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Sub-activity
ODP-Definition: A subgraph of an activity which is itself an activity
and which satisfies the following condition. For any pair of fork-join
actions in the parent activity, if one of these actions is
included in the subgraph, then both must be included
in the subgraph.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
Subclass/Superclass
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.10
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Subclass/Superclass
ODP-Definition: One
class A is a subclass of another class B, and B is a superclass
of A, precisely when the type associated with A is a subtype of
the type associated with B.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.10.4
ODP-Category: Organizational
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Subdomain
ODP-Definition: A domain
which is a subset of a given domain.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
Subtype/Supertype
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.9
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Subtype/Supertype
ODP-Definition: A type
A is a subtype of a type B, and B is a supertype
of A, if every <X> which satisfies A also satisfies B.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.6.5
ODP-Category: Basic
Interpretation Concepts
ODP-Concept: System
ODP-Definition: Something
of interest as a whole or as comprised of parts. Therefore a system may be
referred to as an entity. A component of a system may itself be a
system, in which case it may be called a subsystem.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.1.1.5
ODP-Category: Viewpoint
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Technology viewpoint
ODP-Definition: A viewpoint
on an ODP system and its environment that focuses on the choice of technology
in that system.
Status: Mapped.
UML-Reference: 2.6.2.5
UML-Mapping: Technology
recommendations are made through the use of Tagged Value references.
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.11
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: <X> Template
ODP-Definition: The
specification of the common features of a collection of <X>s in
sufficient detail that an <X> can be instantiated using it. <X> can
be anything that has a type.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.20
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Template class (of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: The
set of all <X>s satisfying an <X> template type, i.e. the
set of <X>s which are instances of the <X> template.
<X> can be anything that has a type.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.19
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Template type
(of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: A
predicate defined in a template that holds for all the instantiations
of the template and that expresses the requirements the instantiations
of the template are intended to fulfill.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.7.1
ODP-Category: Basic
Linguistic Concepts
ODP-Concept: Term
ODP-Definition: A
linguistic construct which may be used to refer to an entity.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.2.5
ODP-Category: Contractual
Behavior
ODP-Concept: Terminating behavior
ODP-Definition: The
behavior which breaks down a liaison and repudiates the
corresponding contractual context and the corresponding contract.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.15.2
ODP-Category: Testing
ODP-Concept: Testing
ODP-Definition: The
truth of a statement in an implementation can only be determined by
testing and is based on a mapping from terms in the specification to
observable aspects of the implementation.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.1.2
ODP-Category: Activity
Structure
ODP-Concept: Thread
ODP-Definition: A chain
of actions, where at least one object participates in all the actions
of the chain.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.6
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Trace
ODP-Definition: A
record of an object’s interactions, from its initial state to
some other state.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: -
ODP-Category: Establishing
Behaviors
ODP-Concept: Trading
ODP-Definition: The
interaction between objects in which information about new or potential contracts
is exchanged via a third party object. Trading involves: a) exporting:
the provision of an identifier to an interface which is claimed
to meet some statement of requirements (i.e. offer a potential contract);
b) importing: the provision of an identifier to an interface
which matches a given statement of requirements, allowing a future binding
behavior to take place (i.e. the establishment of a contract).
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.4.1.8
ODP-Category: Transparencies
ODP-Concept: Transaction transparency
ODP-Definition: A distribution
transparency which masks coordination of activities amongst a
configuration of objects to achieve consistency.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.9.7
ODP-Category: Specification
Concepts
ODP-Concept: Type (of an <X>)
ODP-Definition: A
predicate characterizing a collection of <X>s. An <X> is of the type,
or satisfies the type, if the predicate holds for that <X>. In RM-ODP,
types are needed for, at least, objects, interfaces and actions.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping: An
ODP object type is modeled as a UML class with stereotype, «type».
ODP-Reference: 10746-2.13.4.4
ODP-Category: Establishing
Behaviors
ODP-Concept: Unbinding behavior
ODP-Definition: A behavior
that terminates a binding, i.e. a terminating behavior for the binding.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 10746-3.4.2.1.1
ODP-Category: ODP
Viewpoint Languages
ODP-Concept: <Viewpoint> language
ODP-Definition: Definitions
of concepts and rules for the specification of an ODP system from the
<viewpoint> viewpoint; thus: engineering language: definitions of
concepts and rules for the specification of an ODP system from the engineering
viewpoint.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
ODP-Reference: 15414-6.4.3
ODP-Category: Enterprise
Policy Concepts
ODP-Concept: Violation
ODP-Definition: An action contrary to
a rule.
Status: Unmapped.
UML-Reference:
UML-Mapping:
A
Abstraction, 1
Access transparency, 1
Action, 2
Activity, 3
Actor (with respect to an action), 4
Agent, 4
Announcement, 4
Application management, 5
Architecture (of a system), 5
Artifact (with respect to an action),
5
Atomicity, 5
Authorization, 6
B
Basic engineering object, 6
Behavior (of an object), 6
Behavioral compatibility, 6
Binder, 6
Binding, 7
Binding Behavior, 7
Binding endpoint identifier, 7
Binding object, 7
Binding precondition, 8
C
Capsule, 8
Capsule manager, 8
Chain (of actions), 9
Channel, 9
Checkpoint, 10
Check-pointing, 10
Class (of <X>s), 10
Client object, 10
Cloning, 11
Cluster, 11
Cluster checkpoint, 11
Cluster manager, 11
Cluster template, 12
Commitment, 12
Communication, 12
Communication interface, 12
Communication management, 13
Communications domain, 13
Community, 14
Community object, 14
Compliance, 15
Composite object, 15
Composition (of behaviors), 15
Composition (of objects), 15
Computational interface template, 16
Computational object template, 16
Computational viewpoint, 16
Configuration, 17
Conformance, 17
Conformance point, 17
Consumer object (with respect to a communication), 18
Contract, 19
Contracting party (with respect to a contract), 20
Contractual context, 20
Creation (of an <X>), 20
D
Deactivation, 20
Declaration, 21
Decomposition (of a behavior), 21
Decomposition (of an object), 21
Delegation, 21
Deletion (of an <X>), 22
Derived class/ Base class, 22
Distribution transparency, 22
Dividing action, 22
Domain, 23
Dynamic schema, 23
E
Enabled behavior, 23
Engineering interface reference, 23
Engineering interface reference management domain, 24
Engineering interface reference management policy, 24
Engineering viewpoint, 25
Enterprise viewpoint, 26
Entity, 27
Environment (of an object), 28
Environment contract, 28
Epoch, 28
Error, 29
Establishing behavior, 29
Evaluation, 29
F
Failure, 29
Failure transparency, 30
Fault, 30
Federation, 30
Field of Application (of a specification), 30
Flow, 31
Forking action, 32
G
Group, 32
H
Head action, 33
I
Identifier, 33
Implementable standard, 34
Implementation, 34
Information viewpoint, 35
Initiating object (with respect to a communication), 35
Instance, 36
Instantiation (of an <X> Template), 36
Interaction point, 36
Interceptor, 36
Interchange reference point, 37
Interface, 38
Interface role, 38
Interface signature, 38
Interrogation, 39
Inter-working reference point, 39
Introduction (of an <X>), 39
Invariant, 40
Invariant schema, 41
Isochronicity, 42
IXIT, 42
J
Joining action, 42
L
Liaison, 42
Location in space, 43
Location in time, 43
Location transparence, 43
M
Managed role, 43
Management information, 44
Managing role, 44
Migration, 44
Migration transparency, 45
N
Name, 45
Name resolution, 45
Name space, 45
Naming action, 46
Naming context, 46
Naming domain, 46
Naming graph, 46
Node, 47
Notification, 47
Nucleus, 47
O
Object, 47
Objective, 48
Obligation, 49
Operation, 50
Operation interface, 50
Operation interface signature, 50
P
Party, 51
Perceptual reference point, 51
Permission, 52
Persistence, 53
Persistence transparency, 53
Policy, 54
Post-condition, 55
Precondition, 55
Prescription, 55
Principal, 55
Process, 56
Producer object (with respect to a communication), 57
Programmatic reference point, 58
Prohibition, 59
Proposition, 60
Protocol object, 60
Q
Quality of Service, 60
R
Reactivation, 60
Recovery, 61
Reference point, 61
Refinement, 61
Relocation transparency, 61
Replication transparency, 62
Resource, 62
Responding object, 62
Role, 63
S
Scope (of a system), 63
Sentence, 63
Server object, 64
Signal, 64
Signal interface, 64
Signal interface signature, 64
Spawn action, 65
Stability, 65
State (of an object), 65
Static schema, 65
Step, 66
Stream interface, 66
Stream interface signature, 66
Stub, 67
Sub-activity, 67
Subclass/Superclass, 67
Subdomain, 67
Subtype/Supertype, 68
System, 68
T
Technology viewpoint, 68
Template, 68
Template class (of an <X>), 69
Template type (of an <X>), 69
Term, 69
Terminating behavior, 69
Testing, 70
Thread, 70
Trace, 70
Trading, 70
Transaction transparency, 71
Type (of an <X>), 71
U
Unbinding behavior, 71
V
Viewpoint language, 71
Violation, 72
4.
Janis R. Putman, Architecting with RM-ODP,
Prentice Hall PTR, 2001.
5.
OMG, Unified Modeling Language Specification,
Version 1.4 – 2001.
6.
“Relationship
of the Unified Modeling Language to the Reference Model of Open Distributed
Computing”, OMG, version 1.4,